Introduction
- Install Postgresql Mac Catalina
- Install Postgresql Mac Catalina Download
- Install Postgresql Mac Catalina 2019
I am installing PostgreSQL (V 9.6.16) on macOS Catalina 10.15.1. Before it finishes installing I am getting the following error: Problem running post-install step. Installation may not complete. How to install PostgreSQL 9.6 on Mac OS X (10.7 or later) PostgreSQL is an open source relational database system that has been around for well over a decade and has proven to be a great all around storage choice when developing a web application. I recently upgraded to macOS Catalina and needed to reinstall PostgreSQL via Homebrew. The usual process is simple enough: brew install postgresql does the bulk of the work, and then running brew services start postgres would normally result in Homebrew’s service manager loading the appropriate launch agent for you.
If you’re planning to run PostgreSQL on a Mac, it’s important to know how to install it properly. There are three common ways to install Postgres on a Mac: using Homebrew’s brew install command, downloading the DMG interactive installer for Postgres.app or using MacPorts. In this article, we’ll provide step-by-step instruction for all three of these methods, so you can choose the installation process that works best for you.
Prerequisites
Before attempting the instructions provided in this tutorial, make sure your Mac is running a supported version of MacOS X with at least 256MB of free disk space.
Install PostgreSQL on a Mac
As we mentioned earlier, there are three common ways to install PostgreSQL on macOS. You can use a downloadable DMG installer from Postgres.app, a Homebrew repository for Postgres or a MacPorts installation that uses the port command line interface.
It’s also possible to build a binary of PostgreSQL from source using a tarball archive or to run Postgres in a Docker container; however, we won’t be providing instructions for these alternatives in this article.
Install Postgres using the Postgres.app
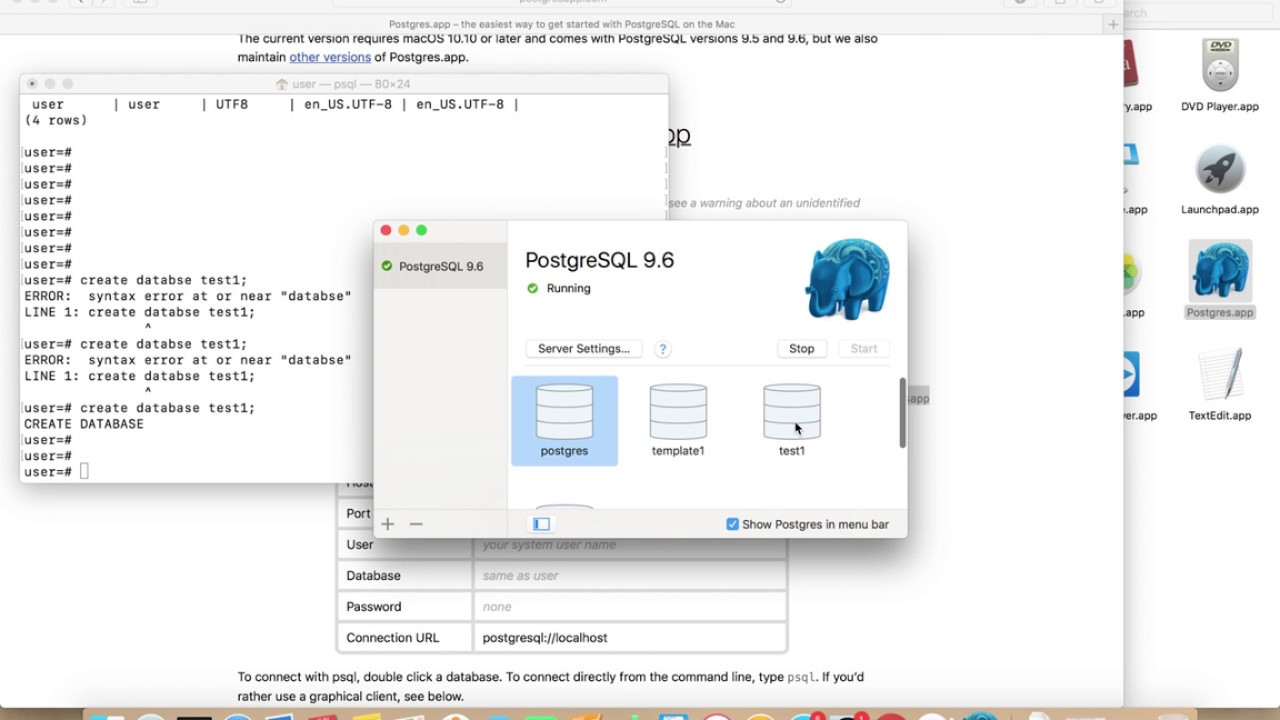
The easiest way to install Postgres on a Mac is to visit the Postgres.app downloads page and get the latest stable version of PostgreSQL as a DMG interactive installer.
Once the download is complete, navigate to your Downloads directory in a Finder window and then double-click on the DMG file to mount the installer. After mounting it, you should see a window pop up that will allow you to drag and drop the Postgres.app to your Applications folder.
Once you complete the installation steps, you should be able to run PostgreSQL by double-clicking the app’s icon in the Applications folder. You can also choose to have Postgres.app run by default– just add the application to your Login Items list in System Preferences.
Use the following export command in a macOS Terminal window to add the Postgres.app path to your current PATH environment variable:
export PATH='/Applications/Postgres.app/Contents/Versions/11/bin:$PATH' |
Install PostgreSQL using Homebrew
If you’d prefer to use Homebrew to install Postgres, you can do so using the brew install command. You’ll need to install the latest version of Homebrew using Ruby if you haven’t already. To do this, use the following command:
/usr/bin/ruby -e'$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/master/install)' |
If you’re running the latest Catalina version of macOS, the output of this command should look like the following:
> This script will install: /usr/local/bin/brew /usr/local/share/doc/homebrew /usr/local/share/man/man1/brew.1 /usr/local/share/zsh/site-functions/_brew /usr/local/etc/bash_completion.d/brew /usr/local/Homebrew |
It may take a few minutes to install Homebrew depending on your internet connection. When the installation is complete, the next step is to “doctor” the Homebrew installation and update its repositories with this compound command:
NOTE: The latest versions of Homebrew will update the repository before installing packages.
Mac install of Postgres using ‘brew’
Now that we’ve installed the latest version of Homebrew, we can use the brew install command to install PostgreSQL:
brew install postgresql |
NOTE: In Homebrew, the postgres “keg” is simply an alias for postgresql, so brew install postgres will work the same way.
Once the installation is finished, you can use the postgres -V or psql -V commands to return the version number and verify that the installation was successful. You can also use the brew list command to view a list of all locally installed packages using Homebrew.
psql command not found
If you get an error stating psql: command not found, you may have to export the path for the Homebrew installation using the following command:
As an alternative, you can also add the following PATH line to your ~/.bash_profile, ~/.bashrc or ~/.zprofile file:
PATH='/Library/PostgreSQL/11/bin:$PATH' |
After editing any of these files, be sure to save the changes. You can have the new settings take effect by running the source command followed by the file name:
Try executing the psql command again after making these changes to verify that the PATH for PostgreSQL and psql has been set.
Start the Postgres server
With Homebrew, you can use the brew services start command to have Postgres start in the background:
brew services start postgresql |
If you’d prefer to run Postgres as a temporary background service, use the following pg_ctl command instead:
You can use Homebrew’s enable command to have PostgreSQL start automatically whenever you restart your Mac:
brew services enable postgresql |
Reinstall PostgreSQL using Homebrew
If you already have PostgreSQL on your Mac and you’d like to reinstall the latest version of it, you can also use Homebrew’s reinstall command:
Install Postgres using MacPorts
The last method we’ll discuss in this article involves using the MacPorts package manager for macOS. To install Postgres on a Mac this way, visit the release page for MacPorts and download a .pkg installer that matches your version of macOS. Once the download is complete, you can navigate to your Downloads directory in a Finder window and double-click the package installer. Follow the steps for the interactive installer, and open a terminal window when you’re done.
NOTE: MacPorts also requires the Xcode library.
Install Postgresql Mac Catalina
In order to install a package, you’ll need to export a path for Macport’s port command. Execute the following export command in a terminal window:
exportPATH=/opt/local/bin:/opt/local/sbin:$PATH /opt/local/bin |
You can also open your .bash_profile or .zprofile file and append the following:
After saving your changes to the file, go back to your terminal and input source ~/.bash_profile or source ~/.zprofile to load the changes.

Use Macport’s ‘port’ command to install Postgres
At this point, we’re ready to use the port command to install Postgres. Use the following port info command to look for the PostgreSQL package:
port info postgresql_select |
You should receive a response that looks like the following:
Now, use the port install command with sudo to install the PostgreSQL packages with elevated privilages:
sudo port install postgresql11 postgresql11-server |
NOTE: You’ll need to press return or type y to verify that you’d like to install the package and its dependencies.
Finally, use the select command shown below to verify that PostgreSQL installed correctly:
If you’re in the MacPort interface, you can just type q to quit.
Uninstall Postgres on a Mac
If you need to uninstall a Homebrew installation of PostgreSQL, use the following command to force the uninstall, even if it depends on other packages:
brew uninstall --ignore-dependencies postgresql |
If you’d like to see any existing PostgreSQL dependencies, use the command shown below:
Uninstall Postgres.app on a Mac
You can uninstall the Postgres.app installation of PostgreSQL the same way you would for any package or applicaton on a Mac– just drag and drop the application from the Applications folder to the Trash directory. Make sure to first shut down the Postgres application and server before attempting this.
Install Postgresql Mac Catalina Download
Uninstall the MacPorts installation of Postgres
If you installed Postgres using MacPorts, you’ll need to use the following command to remove the package:
sudo port uninstall postgres |
Conclusion
If you need to install PostgreSQL on a Mac, it’s good to know the different methods that are available. In this article, we provided instructions on three common installation methods: using the Homebrew package manager, using the interactive installer and using MacPorts. With this tutorial to guide you, you’ll be able to select any of these methods for your own PostgreSQL installation.
Table of Contents
- system settings
- homebrew
- packages in 3rd party taps
- python
Another installation of my personal notes for setting up a new (orcleanly installed) MacOS computer. The process changes just a bit witheach new OS version. This time I will try really hard to reproduce thesteps in order.
I definitely carry some things over from my old computer, but it'spretty minimal. Here's the command to gather up what I need to transfer.
It's also handy to know all of the projects I'm working on:
Note that none of these steps require an Apple ID - I held off onsigning in until the very end just to see if it was possible.
system settings
turn off spelling autocorrect
unmap Control + left,right
I use Control plus the left and right arrow keys to move betweenwindows in emacs and tmux.
Turn on FileVault
I used a recovery key option rather than iCloud for my work machine, iCloud for personal
Developer tools
Pretty much the first thing that needs to happen. This can be donefrom the command line:
homebrew
Homebrew no longer requires user-ownership of /usr/local, so thingsare pretty easy now:
homebrew API token
Apparently lots of requests to GutHub via homebrew can hit a rate limit. There's a higher limit if you create an API token. See https://gist.github.com/christopheranderton/8644743
Here's the url for the token creation dialog:
Make sure that all 'scopes' are unchecked. Once you generate the token, add to your shell profile:
CLI applications
Many packages are installed later with additional elaboration or in asdependencies for other applications; here are some more or lessstandalone packages that I routinely install.
desktop applications
Homebrew installs desktop apps too!
Some of the above (eg, sizeup, dropbox, dash) require licenses andcredentials that must be installed interactively.
packages in 3rd party taps
saml2aws
iTerm2
The homebrew version gave an error on launch with a message about notbeing supported on Catalina, and rather than fight with it, I justdownloaded an installer from the project site.
Update a few settings.
Preferences –> Profiles –> Keys and do these things:
- select 'Left/right option key acts as': +Esc
- + –> Keyboard shortcut 'OPT+<left arrow>': Send Escape sequence 'b'
- + –> Keyboard shortcut 'OPT+<right arrow>': Send Escape sequence 'f'
Default appearance:
- Preferences –> Profiles –> Colors –> Color Presets –> Light Background
- Preferences –> Profiles –> Text –> Change Font –> 14 point
python
My version of Catalina provided Python 2.7.16 and 3.7.3, so let's usehomebrew to get recent version of python3.
I try to limit packages installed to the system to utilities that arevery frequently used outside of the context of a virtualenv.
Seehttps://github.com/Homebrew/homebrew/blob/master/share/doc/homebrew/Homebrew-and-Python.md
dependencies
Run brew info python for required and optional dependencies
Note that 'python' corresponds to the python3 homebrew recipe.
A limited selection of packages - better to use virtualenvs!
emacs
Install Postgresql Mac Catalina 2019

Install latest emacs binary from http://emacsformacosx.com/
Emacs needs a few homebrew packages
Check out my .emacs.d and run setup scripts.
Run setup scripts:
zsh
Install zsh with Homebrew
Change shell to zsh
Install my dotfiles (relevant only to me)
R
I had to give up on installing R with homebrew because it seemed toresult in an interpreter that always wanted to install packages fromsource. So I used the binary from https://cran.r-project.org/bin/macosx/
Some packages that I know I'll need:
Wow, this takes a long time!
Also:
postgresql
This installs multiple versions of postgres. You'll need to add thepath to the CLI for the version you want to use to your PATH, eg:
X11
install Xquartz
X11 key bindings so that the option key is used for Meta. Not sorelevant any more now that I rarely use emacs via X11 for remotesessions.